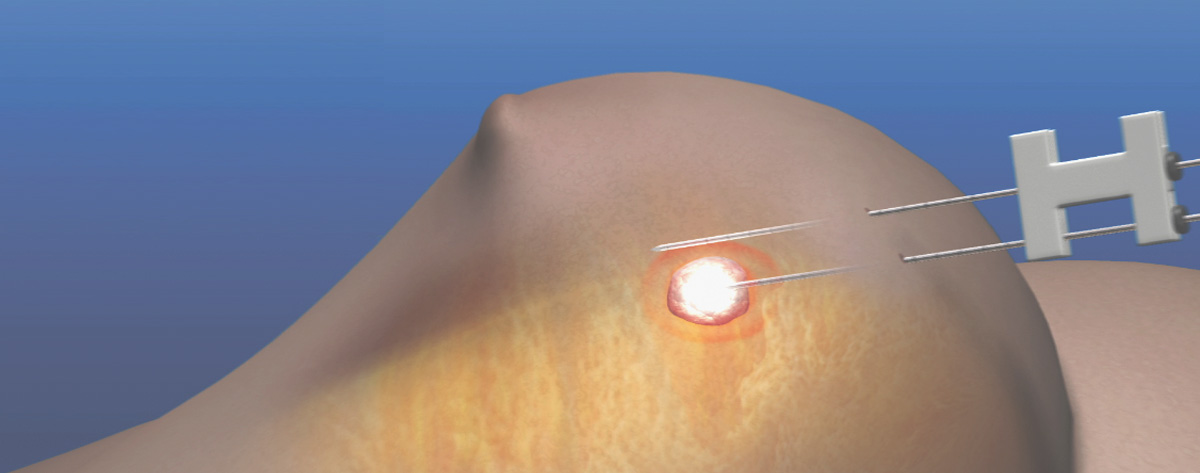
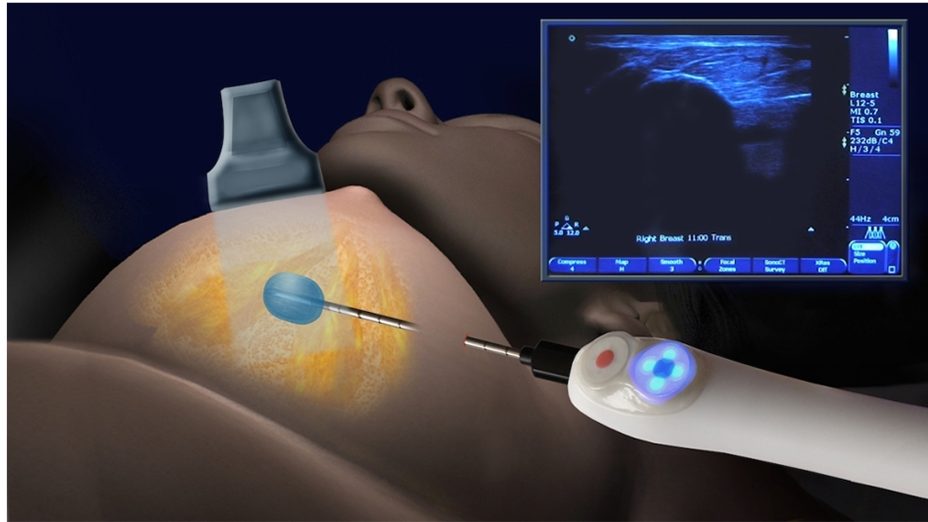
Cryoablation therapy in breast fibroadenomas is a method approved by the FDA in 2002. In cryoablation, the mass is reached with a fine needle and cooled down to -80 degrees. Due to freezing, the cells in the fibroadenoma die and the mass shrinks within months and becomes intangible. The disadvantage is that it is expensive and it takes a long time for the mass to disappear. Before the treatment of fibroadenoma with ablation, it is absolutely necessary to make sure of the diagnosis by performing a biopsy.
In the cryoablation method, it is an ablation method that destroys the cancer by freezing it, not heating it. For this freezing effect to occur, very high pressure Argon gas is passed through the cryoablation needle and released at the very tip of the needle. Argon gas cools down to -40 to -80 degrees in the cancerous tissue and creates an iceball. As a result of this phenomenon, which is called the Joule-Thompson effect, ice crystals form in the tumor due to the ice ball around the cryoablation needle, the vessels are occluded, and a widespread tissue death occurs as a result of apoptosis.
OTHER ABLATION TREATMENTS IN THE BREAST
Fibroadenomas up to 3-4 cm in size can be reduced by using the heat effect in the treatment of fibroadenoma with ablation methods. Thermal Ablation methods are in the form of RF ablation or Laser Ablation methods. Generally, these methods are not preferred for benign tumors. It is mostly used for the reduction of malignant breast tumors. The pinhole used for treatment then heals without leaving any traces. There is an increasing number of publications on the use of ablation methods in the treatment of breast cancers detected at very early stages. This means that we will benefit more from non-surgical treatments for early-stage breast cancers in the near future.
Prof. Dr. Mehmet Mahir Atasoy
Interventional Radiology